SystemML Engine Developer Guide
- Building SystemML
- Testing SystemML
- Development Environment
- Python MLContext API
- Matrix Multiplication Operators
Building SystemML
SystemML is built using Apache Maven. SystemML will build on Linux, MacOS, or Windows, and requires Maven 3 and Java 7 (or higher). To build SystemML, run:
mvn clean package
To build the SystemML distributions, run:
mvn clean package -P distribution
Testing SystemML
SystemML features a comprehensive set of integration tests. To perform these tests, run:
mvn verify
Note: these tests require R to be installed and available as part of the PATH variable on the machine on which you are running these tests.
If required, please install the following packages in R:
install.packages(c("batch", "bitops", "boot", "caTools", "data.table", "doMC", "doSNOW", "ggplot2", "glmnet", "lda", "Matrix", "matrixStats", "moments", "plotrix", "psych", "reshape", "topicmodels", "wordcloud"), dependencies=TRUE)
Development Environment
SystemML itself is written in Java and is managed using Maven. As a result, SystemML can readily be
imported into a standard development environment such as Eclipse and IntelliJ IDEA.
The DMLScript class serves as the main entrypoint to SystemML. Executing
DMLScript with no arguments displays usage information. A script file can be specified using the -f argument.
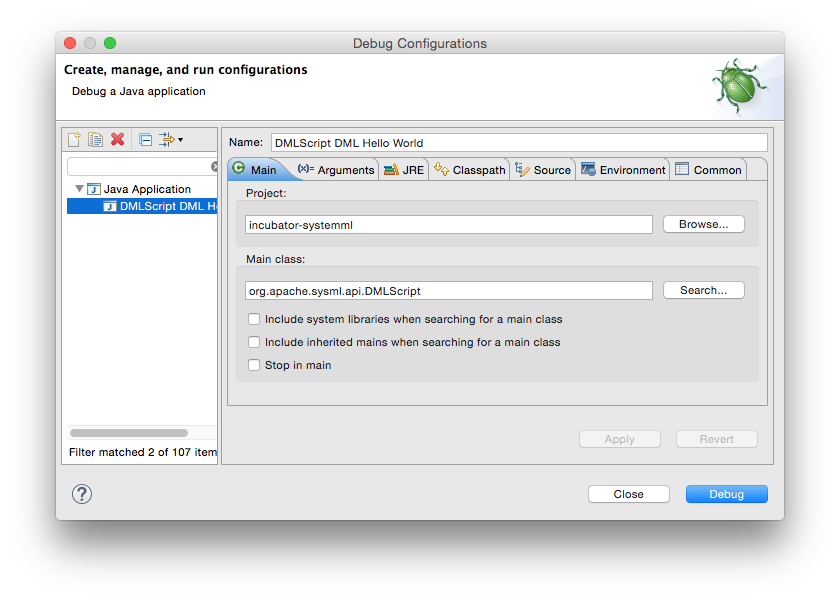
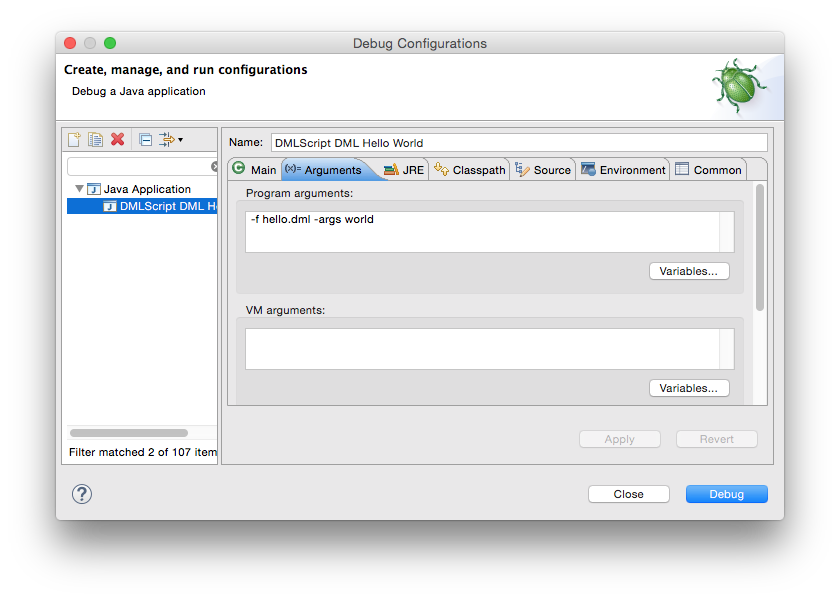
In Eclipse, a Debug Configuration can be created with DMLScript as the Main class and any arguments specified as
Program arguments. A PyDML script requires the addition of a -python switch.
Suppose that we have a hello.dml script containing the following:
print('hello ' + $1)
This SystemML script can be debugged in Eclipse using a Debug Configuration such as the following:
Python MLContext API
When working with the Python MLContext API (see src/main/python/systemml/mlcontext.py) during development,
it can be useful to install the Python MLContext API in editable mode (-e). This allows Python updates
to take effect without requiring the SystemML python artifact to be built and installed.
mvn clean
pip3 install -e src/main/python
mvn clean package
PYSPARK_PYTHON=python3 pyspark --driver-class-path target/SystemML.jarfrom systemml import MLContext, dml
ml = MLContext(sc)
script = dml("print('hello world')")
ml.execute(script)Python 3.5.2 (default, Jul 28 2016, 21:28:07)
[GCC 4.2.1 Compatible Apple LLVM 7.0.2 (clang-700.1.81)] on darwin
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
Using Spark's default log4j profile: org/apache/spark/log4j-defaults.properties
Setting default log level to "WARN".
To adjust logging level use sc.setLogLevel(newLevel). For SparkR, use setLogLevel(newLevel).
17/02/03 12:33:42 WARN NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
17/02/03 12:33:56 WARN ObjectStore: Failed to get database global_temp, returning NoSuchObjectException
Welcome to
____ __
/ __/__ ___ _____/ /__
_\ \/ _ \/ _ `/ __/ '_/
/__ / .__/\_,_/_/ /_/\_\ version 2.1.0
/_/
Using Python version 3.5.2 (default, Jul 28 2016 21:28:07)
SparkSession available as 'spark'.
>>> from systemml import MLContext, dml
>>> ml = MLContext(sc)
Welcome to Apache SystemML!
>>> script = dml("print('hello world')")
>>> ml.execute(script)
hello world
MLResultsMatrix Multiplication Operators
In the following, we give an overview of backend-specific physical matrix multiplication operators in SystemML as well as their internally used matrix multiplication block operations.
Basic Matrix Multiplication Operators
An AggBinaryOp hop can be compiled into the following physical operators.
1. Physical Operators in CP (single node, control program)
| Name | Description | Operation |
|---|---|---|
MM |
basic matrix multiplication | mm |
MMChain |
matrix multiplication chain | mmchain |
TSMM |
transpose-self matrix multiplication | tsmm |
PMM |
permutation matrix multiplication | pmm |
2. Physical Operator in MR (distributed, mapreduce)
| Name | Description | Operation |
|---|---|---|
MapMM |
map-side matrix multiplication, w/ or w/o agg | mm |
MapMMChain |
map-side matrix chain multiplication | mmchain |
TSMM |
map-side transpose-self matrix multiplication | tsmm |
PMM |
map-side permutation matrix multiplication | pmm |
CPMM |
cross-product matrix multiplication, 2 jobs | mm |
RMM |
replication-based matrix multiplication, 1 job | mm |
3. Physical Operators in SPARK (distributed, spark)
| Name | Description | Operation |
|---|---|---|
MapMM |
see MR, flatmap/mappartitions/maptopair + reduce/reducebykey/no_aggregation | mm |
MapMMChain |
see MR, mapvalues/maptopair + reduce | mmchain |
TSMM |
see MR, mapvalues + reduce | tsmm |
PMM |
see MR, flatmaptopair + reducebykey | pmm |
CPMM |
see MR, 2 x maptopair + join + maptopair + reduce/reducebykey | mm |
RMM |
see MR, 2 x flatmap + join + maptopair + reducebykey | mm |
ZIPMM |
partitioning-preserving 1-1 zipping mm, join + mapvalues + reduce | mm |
Complex Matrix Multiplication Operators
A QuaternaryOp hop can be compiled into the following physical operators. Note that wsloss, wsigmoid, wdivmm have different semantics though. The main goal of these operators is to prevent the creation of dense “outer” products via selective computation over a sparse driver (sparse matrix and sparse-safe operation).
1. Physical Operators in CP (single node, control program)
| Name | Description | Operation |
|---|---|---|
WSLoss |
weighted squared loss | wsloss |
WSigmoid |
weighted sigmoid | wsigmoid |
WDivMM |
weighted divide matrix multiplication | wdivmm |
WCeMM |
weighted cross entropy matrix multiplication | wcemm |
WuMM |
weighted unary op matrix multiplication | wumm |
2. Physical Operator in MR (distributed, mapreduce)
| Name | Description | Operation |
|---|---|---|
MapWSLoss |
map-side weighted squared loss | wsloss |
RedWSLoss |
reduce-side weighted squared loss | wsloss |
MapWSigmoid |
map-side weighted sigmoid | wsigmoid |
RedWSigmoid |
reduce-side weighted sigmoid | wsigmoid |
MapWDivMM |
map-side weighted divide matrix mult | wdivmm |
RedWDivMM |
reduce-side weighted divide matrix mult | wdivmm |
MapWCeMM |
map-side weighted cross entr. matrix mult | wcemm |
RedWCeMM |
reduce-side w. cross entr. matrix mult | wcemm |
MapWuMM |
map-side weighted unary op matrix mult | wumm |
RedWuMM |
reduce-side weighted unary op matrix mult | wumm |
3. Physical Operators in SPARK (distributed, spark)
| Name | Description | Operation |
|---|---|---|
MapWSLoss |
see MR, mappartitions + reduce | wsloss |
RedWSLoss |
see MR, 1/2x flatmaptopair + 1-3x join + maptopair + reduce | wsloss |
MapWSigmoid |
see MR, mappartitions | wsigmoid |
RedWSigmoid |
see MR, 1/2x flatmaptopair + 1/2x join + maptopair | wsigmoid |
MapWDivMM |
see MR, mappartitions + reducebykey | wdivmm |
RedWDivMM |
see MR, 1/2x flatmaptopair + 1/2x join + maptopair + reducebykey | wdivmm |
MapWCeMM |
see MR, mappartitions + reduce | wcemm |
RedWCeMM |
see MR, 1/2x flatmaptopair + 1/2x join + maptopair + reduce | wcemm |
MapWuMM |
see MR, mappartitions | wumm |
RedWuMM |
see MR, 1/2x flatmaptopair + 1/2x join + maptopair | wumm |
Core Matrix Multiplication Primitives
| # | Operation | Equations | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | mm |
(a) A%*%B |
- sequential / multi-threaded (same block ops, par over rows in A) - dense-dense, dense-sparse, sparse-dense, sparse-sparse, ultra-sparse - ~20 special cases for matrix-vector, vector-vector, etc |
| 2 | mmchain |
(a) t(X)%*%(X%*%v)(b) t(X)%*%(w*(X%*%v))
|
- sequential / multi-threaded (same block ops, par over rows in X) - dense / sparse x 2 patterns |
| 3 | tsmm |
(a) t(X)%*%X(b) X%*%t(X)
|
- sequential / multi-threaded (same block ops, par over rows in R, 2x tasks) - dense / sparse x 2 patterns; special cases for dot products |
| 4 | pmm |
(a) removeEmpty(diag(v),"rows")%*%X |
- sequential / multi-threaded (same block ops, par over rows in X) - sparse-sparse, dense-dense, sparse-dense |
| 5 | wsloss |
(a) sum(W*(X-U%*%t(V))^2)(b) sum((X-W*(U%*%t(V)))^2)(c) sum((X-(U%*%t(V)))^2))(d) sum(W*(U%*%t(V)-X)^2)(e) sum((W*(U%*%t(V))-X)^2)(f) sum(((U%*%t(V))-X)^2)
|
- sequential / multi-threaded (same block ops, par over rows in W/X) - all dense, sparse-dense factors, sparse/dense-* x 3 patterns - special patterns for (a) and (d) if W is X!=0 |
| 6 | wsigmoid |
(a) W*sigmoid(Y%*%t(X))(b) W*sigmoid(-(Y%*%t(X)))(c) W*log(sigmoid(Y%*%t(X)))(d) W*log(sigmoid(-(Y%*%t(X))))
|
- sequential / multi-threaded (same block ops, par over rows in W) - all dense, sparse-dense factors, sparse/dense-* x 4 patterns |
| 7 | wdivmm |
(a) t(t(U)%*%(W/(U%*%t(V))))(b) (W/(U%*%t(V)))%*%V(c) t(t(U)%*%(W*(U%*%t(V))))(d) (W*(U%*%t(V)))%*%V(e) W*(U%*%t(V))(f) t(t(U)%*%((X!=0)*(U%*%t(V)-X)))(g) (X!=0)*(U%*%t(V)-X)%*%V(h) t(t(U)%*%(W*(U%*%t(V)-X)))(i) (W*(U%*%t(V)-X))%*%V(j) t(t(U)%*%(W/(U%*%t(V)+x)))(k) (W/(U%*%t(V)+x))%*%V
|
- sequential / multi-threaded (same block ops, par over rows in X) - all dense, sparse-dense factors, sparse/dense-* x 9 patterns |
| 8 | wcemm |
(a) sum(X*log(U%*%t(V)))(b) sum(X*log(U%*%t(V)+epsilon))
|
- sequential / multi-threaded (same block ops, par over rows in X) - all dense, sparse-dense factors, sparse/dense-*, 1 pattern |
| 9 | wumm |
(a) X*uop(U%*%t(V))(b) X/uop(U%*%t(V))
|
- any unary operator, e.g., X*exp(U%*%t(V)) or X*(U%*%t(V))^2 - sequential / multi-threaded (same block ops, par over rows in X) - all dense, sparse-dense factors, sparse/dense-*, 2 pattern |